Virtual Reality in Education: Enhancing Learning Experiences
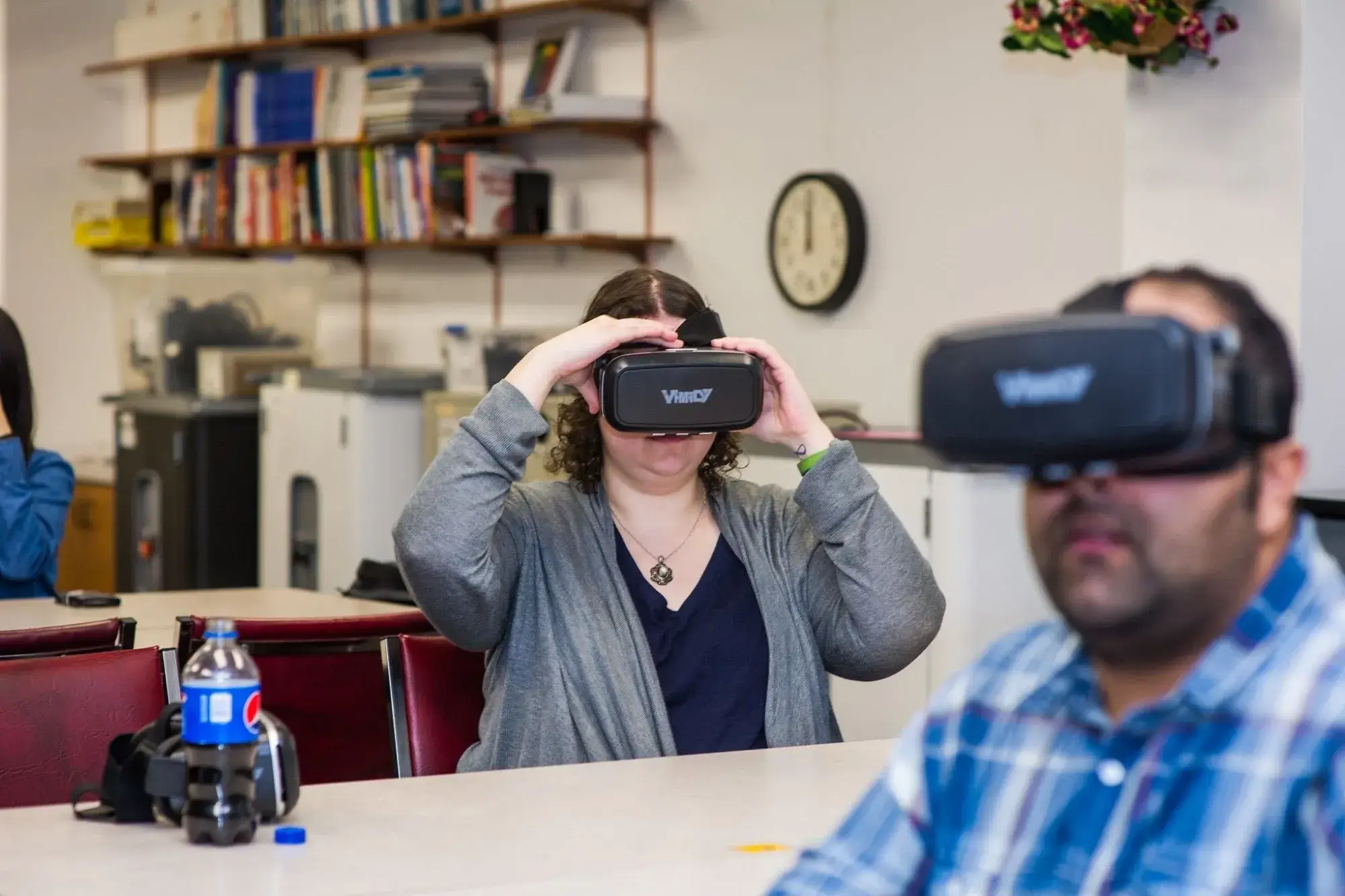
In today’s fast-paced world, technology is transforming every aspect of our lives, including education. One of the most exciting developments is Virtual Reality (VR). Imagine a classroom where students can explore the depths of the ocean, travel back in time to ancient civilizations, or even perform complex surgeries—all without leaving their desks. This is not science fiction; it’s the reality of VR in education. But what makes VR so powerful in the educational sphere, and how can it enhance learning experiences? Let’s dive into this fascinating topic.
What is Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality (VR) is a groundbreaking technological innovation that immerses users in a computer-generated simulation of a three-dimensional environment. Unlike traditional interfaces where users interact with a screen, VR allows users to experience and interact with the digital world as if they were physically present within it. This is achieved through specialized electronic equipment, most notably VR headsets, which are worn over the eyes like a pair of goggles. These headsets display images that simulate depth and perspective, creating the illusion of a real environment that users can explore and interact with. The environments created in VR can vary widely, ranging from exact replicas of real-world locations to entirely fantastical worlds that defy the laws of physics.
How VR Technology Works
The magic of Virtual Reality lies in its ability to immerse users in a digital environment, creating a strong sense of presence—that feeling of actually being in the virtual world. This is primarily achieved through a combination of sensory inputs, with sight and sound being the most critical. The VR headset is equipped with screens and lenses that project a stereoscopic image to each eye, simulating depth and perspective. This visual immersion is further enhanced by head-tracking technology, which monitors the user’s head movements and adjusts the displayed images in real-time. This ensures that the environment changes as the user looks around, maintaining the illusion of a three-dimensional space.
The Evolution of Virtual Reality in Education
Early Uses of VR in Learning
Virtual Reality in education started with very specialized applications, largely due to the high costs and limited technology of early VR systems. These early uses included:
- Flight Simulators: One of the first and most significant applications of VR was in flight training, where pilots could practice flying in a simulated, safe environment.
- Virtual Dissections: In biology classes, VR was used for virtual dissections, allowing students to explore the anatomy of animals without ethical concerns or the need for real specimens.
Current Trends and Advancements
Today, VR in education has advanced significantly, leading to its broader adoption and diverse applications. Some current trends include:
- Interactive History Lessons: Students can virtually visit historical sites or witness significant historical events, making history come alive in a way that textbooks cannot.
- Virtual Science Labs: VR is widely used in science education, particularly in virtual chemistry labs where students can safely conduct experiments without the risks associated with handling real chemicals.
- Affordable VR Headsets: The decrease in the cost of VR headsets has made the technology more accessible to schools and universities, enabling them to integrate VR into their teaching methods more effectively.
This evolution from specialized, costly tools to widely accessible educational resources demonstrates the growing potential of VR to transform learning experiences across various fields.
Benefits of Virtual Reality in Education
Virtual Reality (VR) offers numerous benefits in the educational sphere, enhancing the way students learn and interact with information. These benefits are not just theoretical; they have been demonstrated in classrooms worldwide, where VR has transformed traditional teaching methods.
Immersive Learning Experience
One of the most profound benefits of VR in education is its ability to create immersive learning experiences. Unlike traditional learning methods, where students are often passive recipients of information, VR places them at the center of the experience. This active engagement is particularly powerful in subjects that benefit from visual and experiential learning. For example, in a history lesson about ancient Rome, instead of merely reading about the Roman Forum, students can virtually walk through a reconstruction of the site. They can explore the architecture, witness historical events, and even interact with historical figures, all within a controlled and safe virtual environment. This immersion makes the learning experience more vivid and memorable, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical understanding.
Furthermore, immersive learning through VR allows students to explore subjects in a way that is often not possible in the physical world. For instance, in science education, students can dive into the microscopic world, exploring cell structures or even molecular reactions from the inside. This kind of deep, immersive engagement with the material fosters a more profound understanding and long-term retention of information, as students are not just learning—they are experiencing.
Enhanced Engagement and Motivation
Another significant advantage of VR in education is its ability to enhance student engagement and motivation. Traditional teaching methods can sometimes fail to capture students’ interest, especially in subjects that they find challenging or unappealing. However, VR transforms these potentially mundane lessons into exciting, interactive adventures. By turning learning into a game-like experience, VR naturally appeals to students’ sense of curiosity and play. This shift in how students perceive learning can lead to a dramatic increase in their motivation to study and participate in class.
Moreover, VR is particularly effective in catering to diverse learning styles. While traditional education methods often focus on visual and auditory learning, VR incorporates a kinesthetic element, allowing students to interact physically with the material. This multi-sensory approach ensures that students who might struggle with conventional teaching methods can still engage deeply with the content. For instance, a student who finds it difficult to grasp abstract concepts in mathematics might better understand them through a VR simulation that allows them to manipulate three-dimensional shapes and observe the results in real-time. This inclusivity makes VR a powerful tool for personalized learning, meeting the needs of all students.
Better Retention and Understanding
Studies have consistently shown that VR can significantly improve knowledge retention and understanding. This is largely because VR transforms passive learning into an active, experiential process. When students are merely reading about a concept, they are engaging with it at a surface level. However, when they experience the concept in a virtual environment, they engage with it on multiple levels—visually, auditorily, and kinesthetically. This multi-faceted engagement helps to solidify the information in their minds, leading to better retention over time.
In addition, VR helps to clarify complex or abstract subjects that might be difficult to understand through traditional methods. For example, a biology student might find it challenging to visualize the intricate structures of a cell through textbook diagrams alone. However, a VR simulation that allows them to “enter” the cell and explore its components from the inside provides a level of understanding that is far superior. This hands-on experience not only makes the material more accessible but also more relatable, as students can see how the concepts they are learning apply in a tangible way.
| Benefit/Application | Description | Example | Impact on Learning |
| Immersive Learning Experience | Creates an engaging, hands-on environment where students can actively participate. | Walking through a virtual Roman Forum in a history lesson. | Enhances understanding and retention by making learning more vivid and memorable. |
| Enhanced Engagement and Motivation | Transforms mundane lessons into exciting adventures, appealing to various learning styles. | Virtual simulations in science labs where students can conduct experiments. | Increases student interest and motivation, leading to better academic performance. |
| Better Retention and Understanding | Improves knowledge retention by allowing students to experience concepts directly. | VR simulations of cellular structures in biology. | Clarifies complex subjects, making them more accessible and relatable. |
| Science and Engineering Applications | Simulates complex systems and processes, allowing safe experimentation. | Virtual design and testing of engineering structures. | Provides practical experience without the need for costly or risky materials. |
| Medical and Healthcare Training | Offers realistic simulations of medical procedures and patient interactions. | Virtual surgeries and diagnostic scenarios. | Prepares students for real-life situations with comprehensive, hands-on practice. |
| Arts and Humanities | Brings cultural experiences to life through virtual exploration. | Virtual tours of museums and historical sites. | Deepens understanding and appreciation of cultural and historical contexts. |
Applications of Virtual Reality in Different Educational Fields
VR has found applications across a wide range of educational fields, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness in enhancing learning experiences. Below are detailed explorations of how VR is being used in science, engineering, medical training, arts, and humanities.
VR in Science and Engineering Education
In the fields of science and engineering, VR serves as a powerful tool for simulating complex processes and systems that are difficult to visualize with traditional methods. Engineering students, for example, can use VR to design and test structures in a virtual environment, allowing them to see how their designs hold up under various conditions without the need for physical materials. This not only saves costs but also provides a safe space for experimentation. Students can test their theories, learn from failures, and iterate on their designs in ways that would be impractical or impossible in the real world.
VR also allows science students to conduct experiments that would otherwise be too dangerous, expensive, or time-consuming to perform in a physical laboratory. For instance, in a virtual chemistry lab, students can mix chemicals and observe the reactions without any risk of harm or the need for costly supplies. This ability to perform complex and potentially hazardous experiments safely gives students a deeper understanding of scientific principles and encourages them to explore and experiment without fear of making mistakes.
VR in Medical and Healthcare Training
The integration of VR in medical and healthcare training has been nothing short of revolutionary. Medical students can now practice surgeries, learn anatomy, and diagnose patients in a virtual setting, gaining valuable hands-on experience without the risks associated with real-life procedures. For instance, a VR simulation can allow a student to perform a complex surgical procedure multiple times, honing their skills before they ever touch a real patient. This kind of repetitive practice is crucial in medical training, where the margin for error is often very small.
Moreover, VR can simulate various patient scenarios, allowing students to experience a wide range of medical conditions and emergencies. These simulations can be tailored to include rare conditions that students might not encounter during their standard clinical rotations, ensuring they are well-prepared for any situation. The immersive nature of VR also means that students can practice not just the technical aspects of medicine but also the interpersonal skills required for patient care, such as communication and empathy. This comprehensive training approach helps to produce more competent and confident healthcare professionals.
VR in Arts and Humanities
In the arts and humanities, VR has the potential to bring cultural experiences to life in ways that traditional methods cannot. For example, in a literature class, students might read about the setting of a novel, but with VR, they can actually visit these settings. Imagine studying “Pride and Prejudice” while walking through a virtual representation of the English countryside, or exploring the streets of Paris as depicted in “Les Misérables.” This kind of immersive experience can deepen students’ understanding and appreciation of the texts they are studying, as they are able to contextualize the narrative within its physical and cultural environment.
Similarly, in art history, VR can transport students to virtual museums or historical sites, where they can explore famous artworks and architecture up close. This not only allows for a more interactive and engaging learning experience but also makes these cultural treasures accessible to students who might not have the opportunity to visit them in person. For instance, a student could virtually tour the Louvre in Paris, viewing the Mona Lisa from different angles and learning about the techniques used by Leonardo da Vinci—all without leaving their classroom. This application of VR in the arts and humanities provides students with a richer, more immersive learning experience, bridging the gap between academic study and real-world experience.